Windows airtightness, water resistance and wind load
Windows, doors and skylights provide environmental separation (resistance to water entry, thermal resistance and airtightness), perform a structural function by resisting wind loads, offer stability under operational loads and withstand forced entry.
Windows, doors and skylights in Canada are expected to conform to the Harmonized Standard NAFS—North American Fenestration Standard/Specification for windows, doors, and skylights (A440-11) and the Canadian Supplement: A440S1-09. It replaces a number of Canadian standards that were previously referenced for doors and skylights as well as its window predecessor CSA A440. The primary performance designator required for a window, door or skylight indicates a certain performance level and by itself indicates compliance with the Harmonized Standard.
The Canadian Supplement contains a checklist for selecting performance levels for windows, doors, and skylights. For a window, door or skylight to bear a label in Canada, it must meet all of the applicable requirements of both the Harmonized Standard and the Canadian Supplement, including those pertaining to forced entry.
The Harmonized Standard includes a classification system that rates a window, door or skylight assembly according to airtightness, watertightness and wind load resistance. The ratings achieved are marked on the window, door or skylight and indicate the level of performance that can be expected.
Builders must ensure that windows, doors and skylights are suited for the climates where they will be used by determining the test pressure required (Canadian Supplement) and select fenestration based on the manufacturer’s information, which will meet or exceed the pressure for a given locale.
ENERGY RATING, Windows airtightness, water resistance and wind load
Windows, doors and skylights must have maximum overall thermal transmittance (U) not greater than the values listed in the NBC for the applicable heating-degree day category, or a minimum energy rating not less than the values listed in the NBC (Table 13).
The Energy Rating (ER) is a useful measure of the overall heating season performance of a window based on three factors: (1) solar heat gain; (2) heat loss through frames, spacers and glass; and (3) air leakage heat loss. The ER rating is based on a standard test-size window and depends on the type of window. For example, fixed windows typically have a better (higher) ER rating than operable windows. Because all windows are evaluated the same way, this rating method compares the energy performance of window types made by different manufacturers.
Table 14 compares the thermal efficiencies of several glass configurations. The window industry typically uses U value, which is a measure of thermal transmittance and is the inverse of R value. A U-value indicates the rate of heat transfer through an object. The lower the U-value number, the slower it transfers heat from a warm area to a cold area.
The energy rating (ER) value is calculated using a formula that balances a product’s U-value with its potential solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC) and its airtightness. The higher the ER number, the more energy-efficient the product and the better the product’s thermal performance will be. It is recommended that new windows have an ER of at least 25 for operable windows and at least 33 for fixed windows (or higher, depending on the NBC requirement for your region). This means windows should be at least double-glazed, be low-E coated and have argon gas fill. Higher-efficiency windows are recommended for the colder regions of Canada.
ER is a heating-only rating and therefore achieving a good ER can sometimes result in situations where overheating is a problem. The energy benefit from passive solar heat gain due to a higher ER must be balanced with thermal comfort and impact on cooling.
Required thermal characteristics of windows, doors and skylights
Table 13
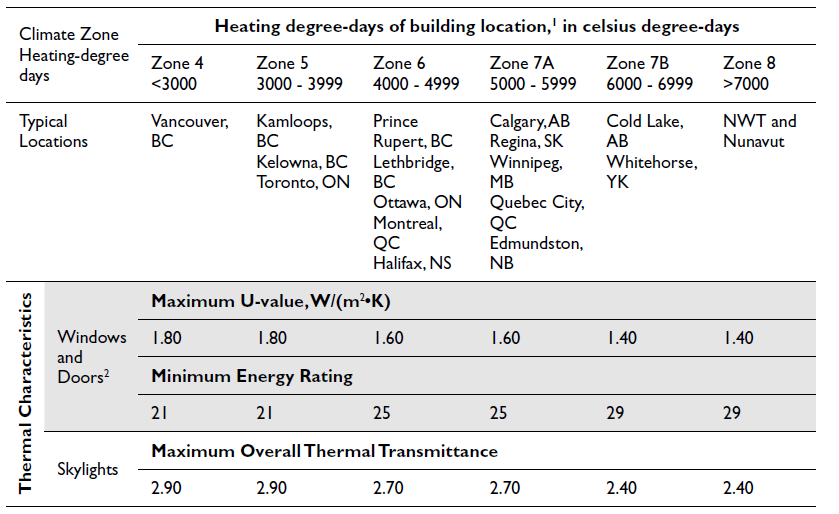
Notes to Table 13
- See NBC 1.1.3.1.
- Except skylights and glass block assemblies
Source : Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation (CMHC)





